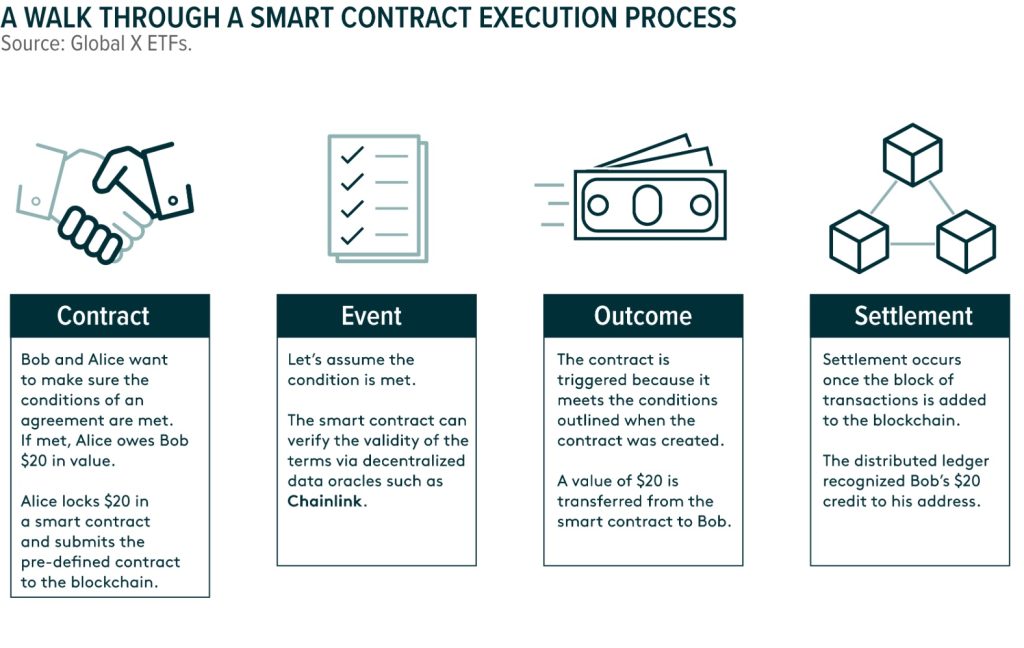
How Smart Contracts Work
A smart contract is a self-executing digital agreement written in code and stored on a blockchain. It automatically carries out actions when specific conditions are met, following simple “if–then” rules (for example: if payment is received, then release the product or service). Once deployed, a smart contract cannot be changed, which makes it transparent and trustworthy. Because it runs on the blockchain, it does not need a bank, lawyer, or other intermediary to enforce the agreement. This reduces costs, speeds up transactions, and limits human error or manipulation.
How Ethereum Is Different from Bitcoin:
Bitcoin was created mainly as digital money and a store of value, similar to digital gold. Its blockchain is optimized for sending and recording Bitcoin transactions securely. Ethereum, on the other hand, was designed as a programmable blockchain. While it also supports a cryptocurrency (Ether), its main purpose is to run smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps). This makes Ethereum more flexible and capable of powering things like decentralized finance (DeFi), NFTs, and automated agreements.
Proof of Work vs Proof of Stake
Bitcoin uses Proof of Work (PoW), where miners compete to solve complex math problems using large amounts of computing power and energy. This process secures the network but is energy-intensive.
Ethereum originally used Proof of Work, but it has switched to Proof of Stake (PoS). In Proof of Stake, validators are chosen to confirm transactions based on how much Ether they “stake” (lock up) as collateral. Proof of Stake uses far less energy, is faster, and allows Ethereum to scale more easily while remaining secure.
How Smart Contracts Work
A smart contract is a self-executing digital agreement written in code and stored on a blockchain. It automatically carries out actions when specific conditions are met, following simple “if–then” rules (for example: if payment is received, thenrelease the product or service). Once deployed, a smart contract cannot be changed, which makes it transparent and trustworthy. Because it runs on the blockchain, it does not need a bank, lawyer, or other intermediary to enforce the agreement. This reduces costs, speeds up transactions, and limits human error or manipulation.
Key Real-World Applications:
- Finance (DeFi): Handle automated lending, borrowing, and tokenized assets (Real World Assets like bonds/real estate).
- Supply Chain: Track products, verify authenticity, automate payments upon delivery, reducing errors and paperwork.
- Insurance: Automatically pay out claims (e.g., flight delays, crop insurance) when conditions (like weather data) are met, reducing fraud and admin costs.
- Healthcare: Securely manage patient data, automate billing, and ensure privacy by controlling access to records.
- Real Estate: Digitize property titles, automate sales, and streamline ownership transfers.
- Digital Assets & Gaming: Power NFTs, manage in-game economies, and create decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs).
- Energy: Facilitate peer-to-peer energy trading.
